

This
publication
has
been developed
by
the U.S.
Department
of
Labor,
Employee Benefits Security Administration
(EBSA).
To
view
this and
other
publications, visit the agency's website
at
dol.gov/ agencies/ebsa.
To order publications, or to speak
with
a benefits advisor, contact
EBSA
at
askebsa.dol.gov.
Or
call
toll
free:
1-866-444-3272
This material
will
be
made
available
in
alternative format
to
persons
with
disabilities
upon
request:
Voice
phone: (202)
693-8644
If
you are deaf, hard
of
hearing,
or
have a speech d isabi I ity, please dial 7-1-1
to access telecommunications relay services.
This
booklet
constitutes a small
entity
comp
I
iance
guide
for
purposes
of
the
Smal I Business Regulatory Enforcement
Fa
irness A
ct
of
1996.

Reporting and Disclosure
Guide for Employee
Benet Plans
U.S. Department of Labor
Employee Benets Security Administration
December 2022

This Reporting and Disclosure Guide for Employee Benet Plans
is a quick reference tool for certain basic reporting and disclosure
requirements under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act
(ERISA). It has been prepared by the U.S. Department of Labor’s
Employee Benets Security Administration (EBSA) with assistance
from the Pension Benet Guaranty Corporation (PBGC).
The rst chapter, beginning on page 2, provides an overview of the
common disclosures that administrators of employee benet plans
are required to give participants, beneciaries, and certain other
individuals under Title I of ERISA. The chapter has three sections.
• Basic Disclosure Requirements for Pension and Welfare Benet
Plans
• Additional Disclosure Requirements for Welfare Benet Plans
That Are Group Health Plans
• Additional Disclosure Requirements for Retirement Plans
The second chapter, beginning on page 17, provides an overview of
reporting and disclosure requirements for dened benet pension
plans under Title IV of ERISA. PBGC administers these provisions.
The chapter focuses primarily on single-employer plans and has
four sections.
• Pension Insurance Premiums
• Standard Terminations
• Distress Terminations
• Reportable Events and Other Reports
The third chapter, beginning on page 21, provides an overview of
the Form 5500 and Form M-1 Annual Reporting requirements. The
chapter consists of two quick reference charts.
Introduction
• Pension and Welfare Benet Plan Form 5500 Quick Reference
Chart
• Form M-1 Quick Reference Chart.
On page 27, there is a list of EBSA and PBGC resources, including
agency websites where laws, regulations, instructions, and other
ocial guidance on ERISA’s reporting and disclosure requirements
are available. Readers should refer to these resources for the
most complete information on ERISA’s reporting and disclosure
requirements.
Not all ERISA reporting and disclosure requirements are reected
in this guide. For example, the guide does not focus on disclosures
required by the Internal Revenue Code or the provisions of ERISA
for which the Department of the Treasury and Internal Revenue
Service (IRS) have regulatory and interpretive authority. For
information on IRS notice and disclosure requirements, please visit
the IRS website at irs.gov/Retirement-Plans/Retirement-Plan-
Reporting-and-Disclosure. This guide also does not focus on new
disclosure requirements added by the Consolidated Appropriations
Act, 2021. For more information on the Consolidated
Appropriations Act, 2021, including the No Surprises Act, see dol.
gov/agencies/ebsa/laws-and-regulations/laws/no-surprises-act.
This Department of Labor publication has been updated as of
December 2022. Please be sure to check EBSA’s website at dol.gov/
ebsa for the current laws and regulations on the reporting and
disclosure provisions included in this publication.
1
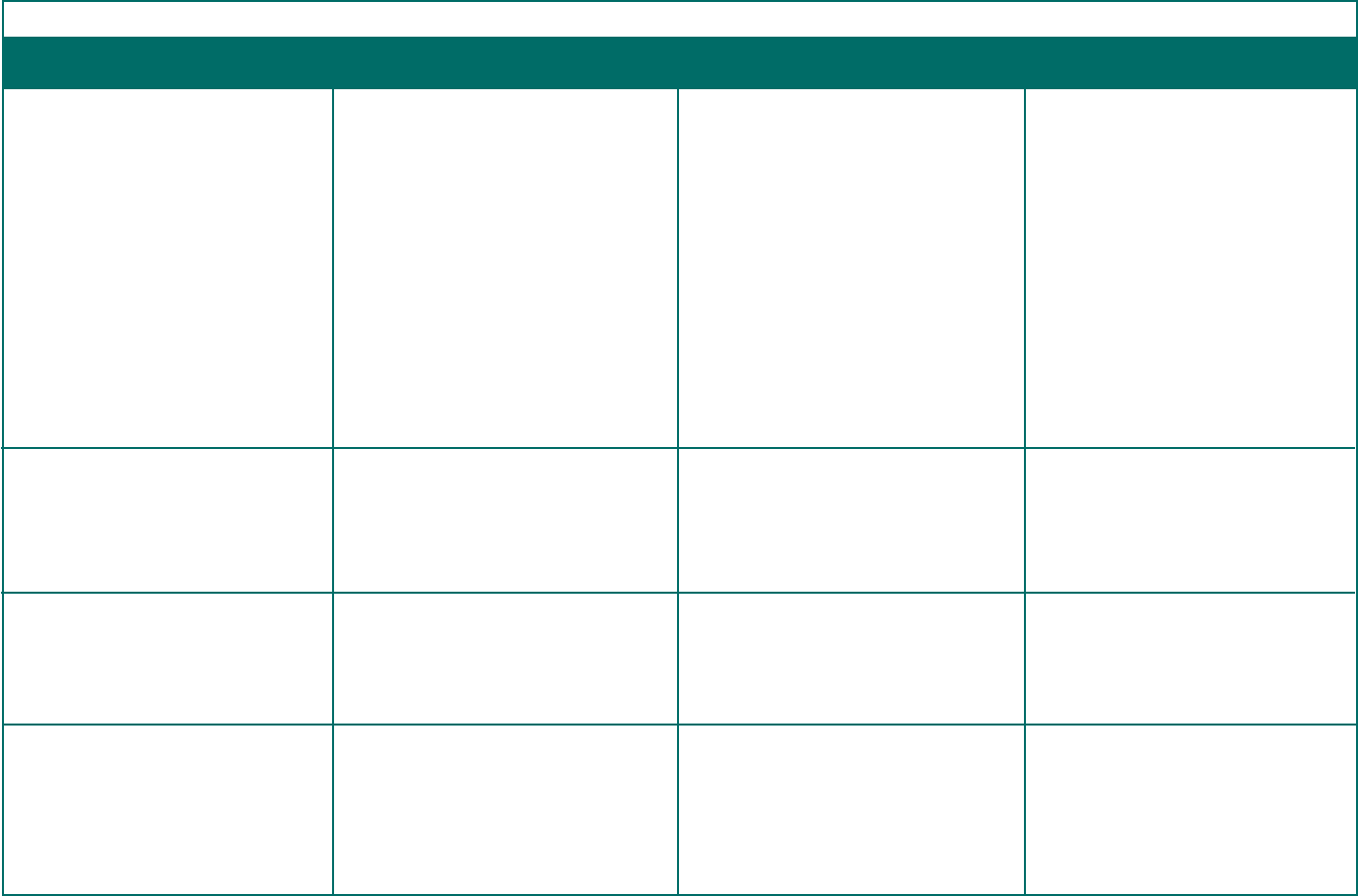
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Overview of ERISA Title I Basic Disclosure Requirements
Summary Plan Description (SPD)
Summary of Material Modication
(SMM)
Summary Annual Report (SAR)
Notication of Benet Determination
(Claims Notices or “Explanation of
Benets”)
The SPD is the primary way to inform
participants and beneciaries about their
plan and how it operates.
It must be wrien for an average participant
and be comprehensive enough to inform
people of their benets, rights, and
obligations under the plan.
Must accurately reect the plan’s contents
and may not contain outdated information
from more than 120 days before its initial
disclosure.
See 29 CFR §§ 2520.102-2 and 2520.102-3 for
style, format, and content requirements.
The SMM describes modications to a
plan and changes to the information that is
required to be in the SPD.
The distribution of an updated SPD satises
this requirement.
See 29 CFR § 2520.104b-3.
The SAR is a narrative summary of the Form
5500.
See 29 CFR § 2520.104b-10(d) for the format.
This notication provides information
regarding benet claim determinations.
Adverse benet determinations must include
the required disclosures (for example, the
specic reason(s) for the denial of a claim, a
reference to the specic plan provisions on
which the benet determination is based,
and a description of the plan’s appeal
procedures).
• Participants
• Beneciaries receiving benets
Also see “Plan Documents” below for
persons who have the right to obtain the
SPD upon request.
See 29 CFR § 2520.102-2(c) for provisions on
foreign language assistance when a portion
of plan participants are only literate in the
same non-English language.
• Participants
• Beneciaries receiving benets
Also see “Plan Documents” below for
persons with the right to obtain SMM upon
request.
• Participants
• Beneciaries receiving benets
The SAR is not required for dened benet
pension plans to which Title IV applies and
that instead provide the annual funding
notice (see below).
Claimants, including:
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• Authorized claims representatives.
To participants: within 90 days of
becoming covered by the plan.
To beneciaries: within 90 days after rst
receiving benets.
A plan has 120 days after becoming subject
to ERISA to distribute the SPD.
Otherwise, once every 5 years for amended
plans.
Once every 10 years for all other plans.
See 29 CFR § 2520.104b-2.
Within 210 days after the end of the plan
year in which the change is adopted.
Within 9 months after the end of the
plan year, or 2 months after the due date
for ling Form 5500 (with an approved
extension).
Requirements vary depending on the
type of plan and the type of benet claim
involved.
See 29 CFR § 2560.503-1 for the claims
procedures requirements.
Section 1: Basic Disclosure Requirements for Retirement and Welfare Benet Plans
2
Note: Plan administrators of retirement plans can provide the relevant disclosures below on paper or furnished electronically. To provide disclosures electronically,
the plan administrator can either post them on a plan website or send them directly to participants, for example, by text message or by email, and must comply with
notication requirements, among other requirements, of the Department’s electronic disclosure regulation. There are a number of protections for participants receiving
electronic disclosures, including the right to request paper copies or to opt out of electronic delivery. The plan administrator also needs to take reasonable steps to protect
the condentiality of participants’ personal information online.
1
Please refer to the Department’s regulations and other guidance for information on the extent to which charges may be assessed to cover the cost of providing particular information, statements, or documents to
participants and beneciaries required under Title I of ERISA. See, e.g., 29 CFR § 2520.104b-30.
1
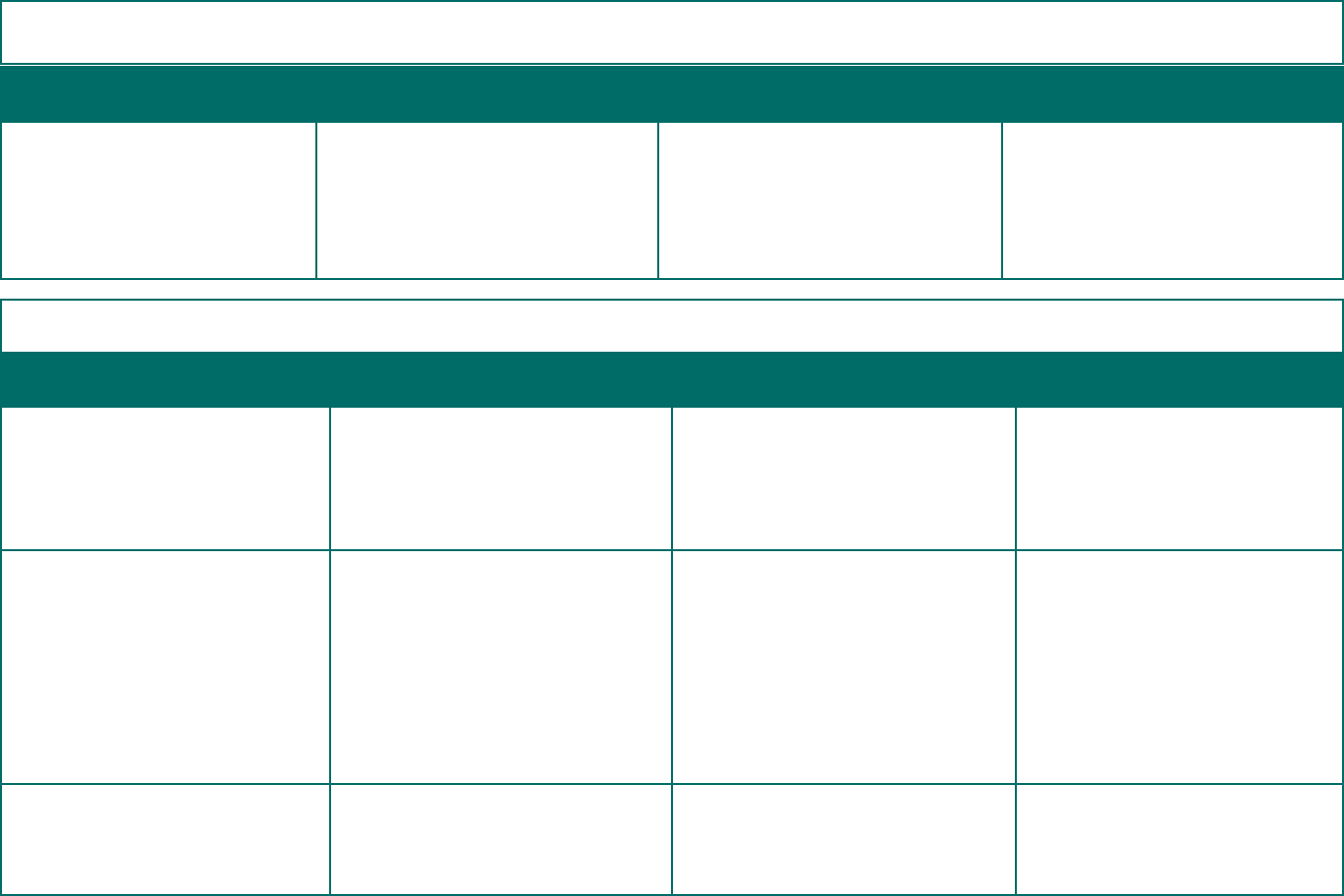
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Document Type of Information To Whom When
2
The term “group health plan” means an employee welfare plan to the extent that the plan provides medical care to employees or their dependents directly or through insurance, reimbursement, or otherwise.
3
COBRA generally applies to group health plans of employers who employed 20 or more employees during the prior calendar year. Provisions of COBRA covering state and local government plans are administered by
the Department of Health and Human Services. COBRA does not apply to plans sponsored by certain church-related organizations.
Plan Documents The plan administrator must provide
copies of certain documents upon wrien
request and must have copies available for
examination.
The documents include the latest updated
SPD, the latest Form 5500, the trust
agreement, and other documents that dictate
how the plan is established or operated.
• Participant
• Beneciaries
Also see 29 CFR § 2520.104a-8 regarding
the Department’s authority to request
documents.
Within 30 days after a wrien request.
Plan administrators must make copies
available at principal oce of the plan
administrator and certain other locations as
specied in 29 CFR § 2520.104b-1(b).
Section 2: Additional Disclosure Requirements for Welfare Benet Plans That Are Group Health Plans
2
3
Section 1: Basic Disclosure Requirements for Retirement and Welfare Benet Plans, continued
Summary of Material Reduction in
Covered Services or Benets
COBRA General Notice
3
COBRA Election Notice
3
This summary explains any group health
plan amendments or changes in information
required to be in SPD that constitute a
“material reduction in covered services or
benets,” such as an increase in premiums
See 29 CFR § 2520.104b-3(d)(3) for
denitions.
This notice informs employees and spouses
of their right to purchase temporary
extension of group health coverage when
coverage is lost due to a qualifying event.
See 29 CFR § 2590.606-1.
For more information, visit dol.gov/
agencies/ebsa/laws-and-regulations/laws/
COBRA.
A model notice is available at dol.gov/sites/
dolgov/les/EBSA/laws-and-regulations/
laws/cobra/model-general-notice.docx.
This notice informs qualied beneciaries
of their right to elect COBRA coverage
when they experience a qualifying event.
It also includes information about other
coverage options available, such as through
a Marketplace.
Participants.
• Covered employees
• Covered spouses
• Covered employees
• Covered spouses
• Dependent children who are qualied
beneciaries
Generally, within 60 days after adopting
a material reduction in group health plan
services or benets.
See 29 CFR § 2520.104b-3(d)(2) for when
a plan may alternatively have 90 days to
provide the required information.
When group health plan coverage begins.
Generally, within 14 days after the
employer or qualied beneciary noties
the plan administrator of the qualifying
event.
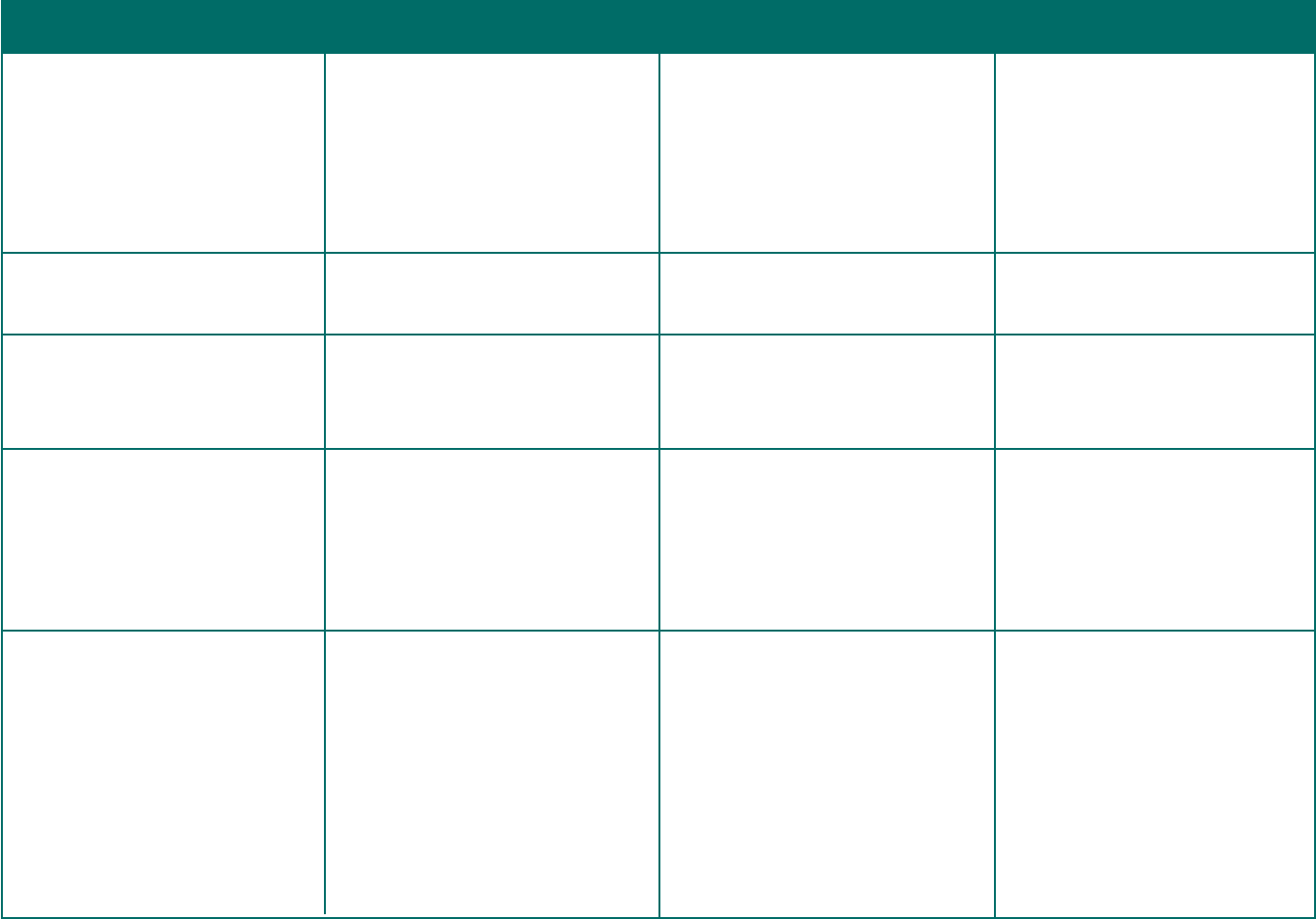
Document Type of Information To Whom WhenDocument Type of Information To Whom When
4
Notice of Unavailability of COBRA
Notice of Early Termination of COBRA
Coverage
Medical Child Support Order (MCSO)
Notice
National Medical Support (NMS)
Notice
See 29 CFR § 2590.606-4.
For more information, visit dol.gov/
agencies/ebsa/laws-and-regulations/laws/
COBRA.
A model notice is available at dol.gov/sites/
dolgov/les/EBSA/laws-and-regulations/
laws/cobra/model-election-notice.docx.
This notice informs an individual that they
are not entitled to COBRA coverage.
See 29 CFR § 2590.606-4(c).
This notice informs a qualied beneciary
that their COBRA coverage will terminate
earlier than the maximum period of
coverage.
See 29 CFR § 2590.606-4(d).
A MCSO notice is a notication from a plan
administrator that states it has received an
order directing the plan to provide health
coverage to a participant’s noncustodial
children and includes the procedures the
plan is required to adopt for determining
whether the MCSO is qualied.
See ERISA § 609(a)(5)(A) for requirements.
An NMS notice is used by the state agency
responsible for enforcing health care
coverage provisions in a MCSO.
See ERISA § 609(a)(5) and 29 CFR §
2590.609-2 for requirements.
Depending upon certain conditions, the
employer must complete and return Part
A of the NMS notice to the state agency, or
it must transfer Part B of the notice to the
plan administrator for a determination on
whether the notice is a qualied MCSO.
Individuals who notify the administrator
of a qualifying event but whom the
administrator determines are not eligible for
COBRA coverage.
Qualied beneciaries whose COBRA
coverage will terminate earlier than the
maximum period of coverage.
• Participants
• Any child named in a MCSO
• The child’s representative
• State agencies
• Employers
• Plan administrators
• Participants
• Custodial parents
• Any child named in a MCSO
• The child’s representative
However, if the employer is also the plan
administrator, the administrator has 44
days after the qualifying event to provide
the notice.
If the plan provides that COBRA
continuation coverage starts on the date of
loss of coverage, the administrator must
provide the notice within 44 days of the
date of loss of coverage due to a qualifying
event.
Generally, within 14 days after being
notied by the individual of the qualifying
event.
As soon as possible after the administrator
determines that coverage will terminate.
The plan administrator must issue
the initial notice, which must include
procedures for determining qualication
promptly after receiving the MCSO.
Then, the administrator must issue a
separate notice of whether the MCSO is
qualied within a reasonable time after
receiving the MCSO.
Within 20 days after the date of the NMS
notice or sooner if reasonable, the employer
must either send Part A to the state agency,
or Part B to the plan administrator.
The administrator must then promptly
notify aected persons of receipt of the
notice and explain the procedures for
determining if it is qualied.
Within 40 business days after the date of
the NMS notice or sooner, if reasonable, the
administrator must complete and return
Part B to the state agency and provide the
required information to aected persons.
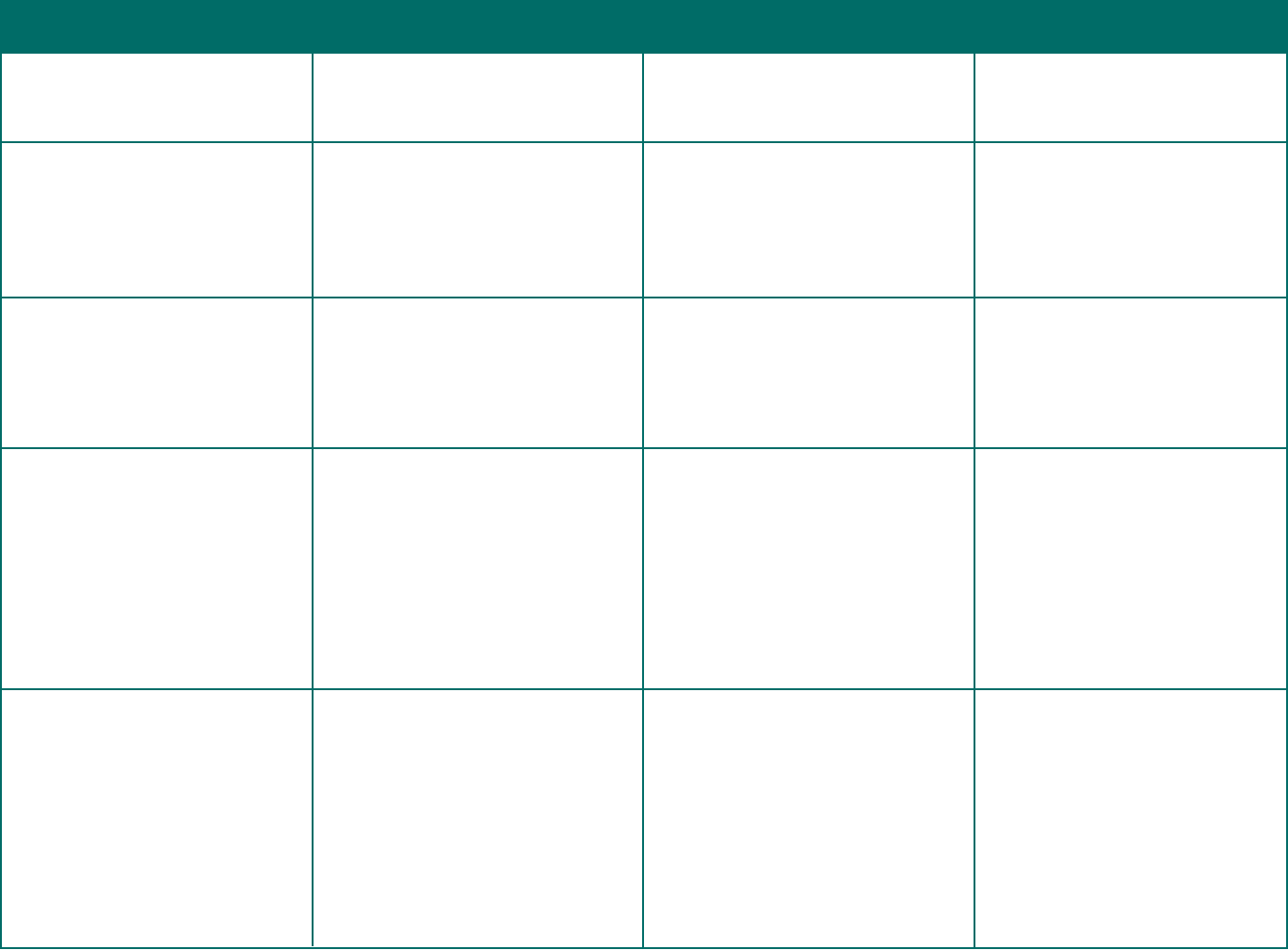
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Notice of Special Enrollment Rights
Employer CHIPRA Notice
Wellness Program Disclosure
Newborns’ Act Description of Rights
This notice describes the group health
plan’s special enrollment rules, including
the eligible employee’s right to special
enroll within 30 days after the loss of
other coverage, marriage, birth of a child,
adoption, or placement for adoption.
See 29 CFR § 2590.701-6(c) for requirements
and a model notice.
The employer must inform employees of
possible premium assistance opportunities
available in the state they reside.
A model CHIPRA notice is available at dol.
gov/sites/dolgov/les/EBSA/laws-and-
regulations/laws/chipra/model-notice.doc.
See 75 FR 5808-11 for more requirements.
This disclosure must be given by any group
health plan that oers a health-contingent
wellness program to obtain a reward.
The notice must disclose the availability
of a reasonable alternative standard or the
possibility that the applicable standard
can be waived. It must also include contact
information to obtain the alternative and
a statement that recommendations of an
individual’s personal physician will be
accommodated.
See 29 CFR § 2590.702(f)(2)(v) for
requirements and model language.
This statement must be included in a
group health plan’s SPD. The statement
must describe the federal or state law
requirements that apply to the plan or
health insurance coverage that relate to a
hospital length of stay in connection with
childbirth.
If the federal law applies in some areas
in which the plan operates and state law
applies in other areas, the statement should
describe the federal or state requirements
applicable to each area.
See 29 CFR § 2520.102-3(u) for requirements
and model language.
Employees eligible to enroll in a group
health plan
All employees, regardless of enrollment or
eligibility status.
Participants and beneciaries eligible to
participate in a health-contingent wellness
program to obtain a reward
Participants
Under certain circumstances, the employer
may be required to send Part A to the state
agency after the plan administrator has
processed Part B.
At or before the date the employee is rst
oered the opportunity to enroll in the
group health plan.
Annually.
In all plan materials that describe the terms
of a health-contingent wellness program
(both activity-only and outcome-based
wellness programs).
For outcome-based wellness programs,
this notice must also be included in any
disclosure that an individual did not
satisfy an initial outcome-based standard.
If the plan materials merely mention that
a program is available, without describing
its terms, this disclosure is not required.
In the Summary Plan Description.
5
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Document Type of Information To Whom When
6
Michelle’s Law Enrollment Notice
Women’s Health and Cancer Rights Act
(WHCRA) Notices
Mental Health Parity and Addiction
Equity Act (MHPAEA) Criteria for
Medically Necessary Determination
Notice
MHPAEA Claims Denial Notice
MHPAEA Increased Cost Exemption
Grandfathered Plan Disclosure/Notice
Summary of Benets and Coverage
(SBC) and Uniform Glossary
This notice must include a description of
the Michelle’s Law provision for continued
coverage during medically necessary leaves of
absence.
See ERISA section 714 (c).
This notice describes required benets for
mastectomy-related reconstructive surgery,
prostheses, and treatment of physical
complications of mastectomy.
This notice must explain the criteria for
medically necessary determinations related to
mental health/substance use disorder benets.
See 29 CFR § 2590.712(d)(1).
This notice must provide the reason for any
denial of reimbursement or payment for
services related to mental health/substance use
disorder benets.
See 29 § CFR 2590.712(d)(2).
A group health plan claiming MHPAEA’s
increased cost exemption must provide a
notice of the plan’s exemption from the parity
requirements.
See 29 CFR § 2590.712(g)(6)
This notice must disclose that the plan is
grandfathered and must include contact
information.
See 29 CFR § 2590.715-1251(a)(2).
The SBC is a template that describes the
benets and coverage under the plan. A
uniform glossary denes important health
coverage and medical terms.
See 29 CFR § 2590.715-2715(a) and (c).
The required SBC template is available at
dol.gov/sites/dolgov/les/EBSA/laws-and-
regulations/laws/aordable-care-act/for-
employers-and-advisers/sbc-template-new.
pdf.
• Participants
• Beneciaries
Participants
• Any current or potential participant
• Beneciary
• Contracting provider
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• EBSA
• State regulators
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• Plans (provided by group health
insurance issuers)
• Participants
• Beneciaries
With any notice regarding a requirement
for certication of student status for
coverage under the plan.
Note that under the Aordable Care Act,
plans cannot deny or restrict coverage
for a child under the age of 26 based on
student status.
Upon enrollment and annually.
Upon request.
Upon request or as otherwise required by
other laws.
If using the cost exemption.
In any plan materials describing the
benets or health coverage.
With enrollment materials and upon
renewal or reissuance of coverage.
To special enrollees by the date the SPD
is required to be provided (90 days from
enrollment).
Also, within 7 days upon request.
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Summary of Benets and Coverage:
Notice of Modication
Notice Regarding Designation of a
Primary Care Provider
The Uniform Glossary is available at dol.
gov/sites/dolgov/les/EBSA/laws-and-
regulations/laws/aordable-care-act/
for-employers-and-advisers/sbc-uniform-
glossary-of-coverage-and-medical-terms-
new.pdf.
The SBC must include both a website
link where an individual can review
the Uniform Glossary as well as contact
information for obtaining a paper copy.
If a plan makes a material modication in
any of the plan terms that would aect the
content of the SBC, the plan must provide
notice of the change.
This does not apply to changes that occur in
connection with a renewal or reissuance.
See 29 CFR § 2590.715-2715(b).
If a non-grandfathered plan requires a
participant or beneciary to designate
a primary care provider, the plan must
provide notice of the terms of the plan
or coverage regarding designation of a
primary care provider. The notice must
include the following:
• Participants have the right to designate
any participating primary care
provider who is available to accept the
participant.
• Participants can designate any
participating pediatrician for a child.
• The plan does not require
authorization or referral for OB/
GYN care by a participating OB/GYN
professional.
See 29 CFR § 2590.715-2719A(a)(4).
For plan years beginning on or after January
1, 2022, grandfathered plans must also
provide this information. See 29 CFR §
2590.722.
Model language is available at dol.gov/sites/
dolgov/les/EBSA/laws-and-regulations/
laws/aordable-care-act/for-employers-
and-advisers/patient-protection-model-
notice.doc.
• Participants
• Beneciaries
Participants
Within 60 days before the date on which
the change will become eective.
With the Summary Plan Description or
any other similar description of benets
7
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Document Type of Information To Whom When
8
Internal Claims and Appeals and
External Review Notices
External Review Process Disclosure
Internal Claims and Appeals
Non-grandfathered plans must provide a
notice of adverse benet determination and
a notice of nal internal adverse benet
determination.
See 29 CFR § 2590.715-2719(b)(2)(ii)(E) for
specic content requirements.
Model notices are available at:
• dol.gov/sites/dolgov/les/EBSA/
laws-and-regulations/laws/aordable-
care-act/for-employers-and-advisers/
revised-model-notice-of-adverse-
benet-determination.doc
• dol.gov/sites/dolgov/les/EBSA/
laws-and-regulations/laws/
aordable-care-act/for-employers-
and-advisers/revised-model-notice-
of-nal-internal-adverse-benet-
determination.doc
External Review
After an external review, the independent
review organization (IRO) will issue a notice
of the nal external review decision.
See 29 CFR § 2590.715-2719 (c) and (d) for
requirements.
For plan years beginning on or after January
1, 2022, the external review requirements,
including the disclosure requirements,
apply to grandfathered plans for claims
subject to the No Surprises Act.
A model notice is available at dol.gov/sites/
dolgov/les/EBSA/laws-and-regulations/
laws/aordable-care-act/for-employers-
and-advisers/revised-model-notice-of-
nal-external-review-decision.doc.
Non-grandfathered plans following a state
external review process must provide a
description of the external review process.
For plan years beginning on or after January
1, 2022, the external review requirements,
including the disclosure requirements,
apply to grandfathered plans for claims
subject to the No Surprises Act.
See 29 CFR § 2590.715-2719(c) for more
information.
For internal claims and appeals:
• Claimants
For external review, by the IRO to:
• Claimants
• The plan
• Participants
• Beneciaries
For internal claims and appeals, the
timing varies based on the type of claim.
For external review, the timing varies
based on the type of claims and whether
the state or the federal process applies.
See 29 CFR § 2590.715-2719 for more
information.
In the SPD, policy, certicate, or other
evidence of coverage.
Document Type of Information To Whom When
EBSA Form 700
Employer Notice to Employees of
Coverage Options
Individual Coverage Health
Reimbursement Arrangement (ICHRA)
Notice
EBSA Form 700 is used to claim an
accommodation from the requirement to
cover certain contraceptive services without
cost-sharing. Other methods to invoke an
accommodation, such as providing a notice
to the Secretary of Health and Human
Services (HHS), are also available.
EBSA Form 700 is available at dol.gov/sites/
dolgov/les/EBSA/laws-and-regulations/
laws/aordable-care-act/for-employers-
and-advisers/ebsa-form-700.pdf.
Information about providing notice to
HHS is available at dol.gov/sites/dolgov/
les/EBSA/laws-and-regulations/laws/
aordable-care-act/for-employers-and-
advisers/model-notice-to-secretary-of-hhs.
pdf.
Employers subject to the Fair Labor
Standards Act must provide a notice
informing the employee of the existence of
the Marketplace, the potential availability of
a tax credit, and that an employee may lose
the employer contribution if the employee
purchases a qualied health plan.
See Technical Release 2013-02 & FLSA 18B
for requirements.
A model notice is available at dol.gov/sites/
dolgov/les/EBSA/laws-and-regulations/
laws/aordable-care-act/for-employers-
and-advisers/model-notice-for-employers-
who-oer-a-health-plan-to-some-or-all-
employees.doc.
This notice informs employees of the
availability of an ICHRA from their
employer and its terms, including the right
to opt out. The notice must describe the
potential availability of the premium tax
credit and explain that if the individual
accepts the ICHRA, the individual will
not be able to claim a premium tax credit
for individual health insurance coverage.
Additionally, the notice must explain
if the ICHRA is considered aordable,
the individual won’t be able to claim a
premium tax credit even if they opt out.
A model notice is available at dol.gov/sites/
dolgov/les/ebsa/laws-and-regulations/
rules-and-regulations/completed-
rulemaking/1210-AB87/individual-
coverage-model-notice.pdf.
For EBSA Form 700:
• The plan’s health insurance issuer
• Third-party administrator
The notice to the Secretary of HHS should
be sent to HHS by email or mail.
All employees, regardless of plan eligibility
or part-time or full-time status.
Participants
When an organization wishes to claim
an accommodation from the requirement
to cover certain contraceptive services
without cost-sharing.
To all new employees.
At least 90 calendar days before the
beginning of each plan year.
For any participant not eligible at the
beginning of the plan year (or not
eligible when the notice is provided to
participants before the beginning of the
plan year): the notice should be provided
by the date when the participant is rst
eligible.
For any participant employed by an
employer that was established less than
120 days before the rst plan year of the
ICHRA: by the date when the participant
is rst eligible.
9
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Transparency in Coverage –
Disclosure to the Public
Transparency in Coverage –
Disclosure to Participants and
Beneciaries
Non-grandfathered plans and issuers must
post on a public website machine-readable
les on network rates and out-of-network
allowed amounts and billed charges for
plan years beginning on or after January 1,
2022.
FAQs Part 49 deferred enforcement of this
requirement until July 1, 2022 (and deferred
enforcement for a machine-readable le on
prescription drugs while the responsible
agencies consider, through notice-and-
comment rulemaking, whether the
requirement remains appropriate).
Non-grandfathered plans and issuers
must provide an online price comparison
tool (and in paper form, upon request)
containing price and provider information
concerning health benets that allows an
individual to compare the cost sharing that
the individual would be responsible for
paying.
July 1, 2022
For plan years beginning on or after
January 1, 2023, the 500 items and
services identied by the Department
of Labor, available at hp://www.cms.
gov/healthplan-price-transparency/
resources/500-items-services. For plan
years beginning on or after January 1,
2024, all covered items or services
The public
• Participants
• Beneciaries
10
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Periodic Pension Benet Statement
(Individual Benet Statement)
Statement of Accrued and
Nonforfeitable Benets
The content of this statement varies
depending on the type of plan.
In general, all statements must indicate total
benets and total nonforfeitable pension
benets, if any, that have accrued, or the
earliest date on which benets become
nonforfeitable.
Benet statements for an individual account
plan must also provide:
• the value of each investment to which
assets in the individual account have
been allocated and
• two illustrations of the account balance
as a stream of estimated monthly
lifetime payments (one as a single life
annuity and one as a qualied joint
and survivor annuity).
Model language is available at dol.gov/
sites/dolgov/les/EBSA/employers-
and-advisers/plan-administration-and-
compliance/retirement/model-benet-
statement-supplement.pdf.
Benet statements for individual account
plans that permit participant investment
direction must also include:
• an explanation of any limitation or
restriction on the participant’s or
beneciary’s rights under the plan to
direct an investment;
• an explanation of the importance of a
well-balanced and diversied portfolio,
including a statement of the risk that
holding more than 20 percent of a
portfolio in the security of an entity
(such as employer securities) may not
be adequately diversied; and
• a notice directing the participant
or beneciary to the Department
of Labor’s website for information
on individual investing and
diversication.
See ERISA § 105.
This statement lists total accrued benets
and total nonforfeitable pension benets, if
any, that have accrued, or the earliest date
on which benets become nonforfeitable.
See ERISA § 209.
• Participants
• Beneciaries
Participants
11
Section 3: Additional Disclosure Requirements for Retirement Plans
For individual account plans that permit
participants to direct their investments
At least once each quarter.
In addition, upon request from a
beneciary who does not receive
statements automatically, limited to one
request during any 12-month period.
For individual account plans that do not
permit participants to direct their
investments
At least once each year.
In addition, upon request from a
beneciary who does not receive
statements automatically, limited to one
request during any 12-month period.
For dened benet plans
At least once every 3 years.
Alternatively, dened benet plans can
satisfy this requirement if at least once
each year the administrator provides
notice of the availability of the pension
benet statement and the ways to obtain
such statement.
In addition, upon wrien request, limited
to one request during any 12-month
period.
Upon request, upon termination of service
with the employer, or after the participant
has a 1-year break in service.
Statements provided upon request are
limited to one request during any
12-month period.
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Suspension of Benets Notice
Notice of Transfer of Excess Pension
Assets to Retiree Health
Benet Account
Domestic Relations Order (DRO)
and Qualied Domestic Relations
Order (QDRO) Notices
Notice of Signicant Reduction in
Future Benet Accruals
Notice of Failure to Meet Minimum
Funding Standards
This notice informs employees that their
benet payments are being suspended
during certain periods of employment or
reemployment.
See 29 CFR § 2530.203-3 for requirements.
This noties stakeholders that dened
benet plan excess assets are being
transferred to a retiree health benet
account.
See ERISA § 101(e) for requirements.
These notices state that a plan administrator
has received a DRO. They must include the
procedures for determining whether a DRO
is qualified and explain whether the
administrator has determined that the DRO
is qualified.
For more information, see ERISA § 206(d)(3)
(G)(i) and the EBSA booklet QDROs: The
Division of Retirement Benefits Through
Qualified Domestic Relations Orders.
This notice explains any plan amendments
to dened benet plans and certain dened
contribution plans that provide for either
a signicant reduction in the rate of future
benet accruals or the elimination or
signicant reduction in an early retirement
benet or retirement-type subsidy.
See 26 CFR § 54.4980F-1 for further
information
This notice declares a failure to make
a required installment or other plan
contribution to satisfy the minimum
funding standard within 60 days of
contribution due date. (Not applicable to
multiemployer plans).
See ERISA § 101(d) for more information.
Employees whose benets are suspended.
The employer sponsoring the pension plan
from which transfer is made must give
notice to:
• The Secretaries of Labor and the
Treasury
• Each employee organization
representing plan participants
• The plan administrator
The plan administrator must notify:
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• Participants
• Alternate payees. For example:
• Spouse
• Former spouse
• Child
• Other dependent of a participant
named in a DRO as having a right
to receive all or a portion of the
participant’s plan benets
• Participants
• Alternate payees under a QDRO
• Contributing employers
• Certain employee organizations
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• Alternative payees under QDROs
12
Only one statement is required if there
are consecutive 1-year breaks in service.
During the rst month or the payroll
period in which the withholding of
benet payments occurs.
Within 60 days before the date of the
transfer.
The employer notice also must be
available for inspection in the principal
oce of the administrator.
The initial notice, which must include
both an acknowledgement that the plan
administrator received a DRO and the
procedures for determining a DRO
qualication, must be issued promptly
after receiving the DRO.
A separate notice of whether the DRO is
qualied must be issued within a
reasonable time after receiving the DRO.
Within a reasonable time, generally 45
days, before the eective date of a plan
amendment subject to ERISA, except as
provided in regulations from the
Secretary of the Treasury.
See § 204(h) of ERISA and IRC § 4980F.
Within a reasonable period of time after
the failure.
Notice is not required if a funding waiver
is requested in a timely manner.
However, if the waiver is denied, the
notice must be provided within 60 days
after the denial.
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• Participants and beneciaries of
individual account plans aected by
such blackout periods
• Issuers of aected employer securities
held by the plan
Participants and beneciaries on whose
behalf an investment in a QDIA may be
made
Each participant to whom the arrangement
applies.
• Participants
• Beneciaries receiving benets
• Alternate payees receiving benets
• Labor organizations representing
participants under the plan
• Each employer of a multiemployer
plan that is a party to a collective
bargaining agreement pursuant to
which a plan is maintained or who
would be subject to withdrawal
liability
13
Section 404(c) Plan Disclosures
Notice of Blackout Period for
Individual Account Plans
Qualied Default Investment
Alternative (QDIA) Notice*
Automatic Contribution
Arrangement
Notice*
Annual Funding Notice
For certain information, before the time
when investment instructions are to be
made.
For other information, upon request.
Generally, at least 30 days but not more
than 60 days advance notice.
• At least 30 days before the date of
plan eligibility, or
• At least 30 days before the date of
any rst investment in a QDIA on
behalf of a participant or bene-
ciary, or
• On or before the date of plan
eligibility if the participant has the
opportunity to make a permissible
withdrawal within the rst 90 days.
Also, annually at least 30 days in advance
of each plan year.
See 29 CFR § 2550.404c-5
Within a reasonable period before the
plan year.
For large plans: Within 120 days after the
plan year.
For small plans: Before the date on which
the annual report is led or before the
latest date the annual report must be led
(including extensions), whichever is
earlier.
A small plan is dened as having 100 or
fewer participants on each day during
the plan year preceding the notice year.
Document Type of Information To Whom When
This notice contains investment-related
and certain other disclosures for
participant-directed individual account
plans described in 29 CFR § 2550.404c-
1. This includes a blackout notice for
participant-directed individual account
plans described in ERISA section 404(c)
(1)(A)(ii), as described below.
Special rules apply for qualied
investment options under ERISA section
404(c)(4)(C).
This notice provides advance notice of
any period of more than 3 consecutive
business days when there is a temporary
suspension, limitation, or restriction
under an individual account plan
on directing or diversifying plan
assets, obtaining loans, or obtaining
distributions.
See ERISA § 101(i) and 29 CFR §
2520.101-3 for further information on the
notice requirement.
This notice informs participants and
beneciaries of:
• the circumstances under which
contributions or other assets will be
invested on their behalf in a QDIA,
• the investment objectives of the
QDIA, and
• the right of participants and
beneciaries to direct investments
out of the QDIA.
See 29 CFR § 2550.404c-5.
See also ERISA § 514(e)(3).
This notice informs participants of
their rights and obligations under an
automatic contribution arrangement.
See ERISA § 514(e)(3).
This notice provides basic information
about the status and nancial condition
of a dened benet pension plan,
including:
• the plan’s funding percentage;
• assets and liabilities;
• demographic information
regarding active, retired, and
separated from service participants;
• the funding policy;
• endangered, critical, or critical and
declining status;
*Use of the IRS sample Automatic Enrollment Notice posted on the IRS website may be used to satisfy these two notice requirements. See Field Assistance Bulletin 2008-03, Question 8.
Document Type of Information To Whom When
• PBGC
• Each employee organization
• Each employer that has an obligation
to contribute to the plan
• Participants
• Beneciaries receiving benets
• Each labor organization representing
participants under the plan
• Each employer that has an obligation
to contribute to the plan
Any employer who has an obligation to
contribute to the plan.
• Participants
• Beneciaries
14
Multiemployer Plan Summary Report
Multiemployer Pension Plan
Information Made Available on Request
Multiemployer Plan Notice of Potential
Withdrawal Liability
Notice of Funding-based Limitation
Within 30 days after the due date of the
annual report.
Within 30 days of wrien request.
A requester is not entitled to receive more
than one copy of any report or applica-
tion during any 12-month period.
Generally, within 180 days of a wrien
request.
Generally, within 30 days after a plan
becomes subject to a specied funding-
based limitation.
Also, any other time determined by the
Secretary of the Treasury.
See IRS Notice 2012-46.
• explanation of events having a
material eect on liabilities or
assets;
• rules on termination or insolvency;
• a description of the benets
guaranteed by PBGC;
• annual report information;
• information disclosed to PBGC, if
applicable; and
• any additional information the
plan administrator elects to
include.
See ERISA § 101(f) and 29 CFR §
2520.101-5.
This report contains certain nancial
information, such as:
• contribution schedules,
• benet formulas,
• number of employers obligated to
contribute,
• number of participants on whose
behalf no contributions were made
for a specied period of time,
• number of withdrawing
employers, and
• withdrawal liability.
See ERISA § 104(d).
This information includes copies of
periodic actuarial reports; quarterly,
semi-annual, or annual nancial
reports; and amortization extension
applications.
See ERISA § 101(k) and 29 CFR §
2520.101-6.
This notice provides an estimated
amount of the employer’s withdrawal
liability and how such estimated
liability was determined.
See ERISA § 101(l).
The plan administrator of a single-
employer or multiple-employer
dened benet plan must provide
a notice of specied funding-based
limits on benet accruals and benet
distributions.
See ERISA § 101(j).
Document
Type of Information
To Whom
When
Notice of Right to Divest
Disclosures required for the Fiduciary
Safe Harbor for Automatic Rollovers
to Individual Retirement Plans for
Certain Mandatory Distributions
Exceeding $1,000.
Notice of Plan Termination pursuant
to the Safe Harbor for Distributions
from Terminated Individual Account
Plans
• Participants
• Alternate payees with accounts
under the plan
• Beneciaries of deceased
participants
See ERISA § 204(j).
Separating participants subject to
mandatory distributions under the
Internal Revenue Code.
Participants or beneciaries in
terminated individual account plans
Within 30 days before the rst date on
which the individuals are eligible to
exercise their rights.
Before mandatory distributions are made.
The disclosure will be sucient if
provided in conjunction with the notice
required under Code section 402(f),
which must be provided to a plan
participant no less than 30 days and no
more than 180 days before the date of a
distribution.
See IRS Notice 2009-68.
During the winding up process of the
plan termination.
Participants and beneciaries have 30
days from the receipt of the notice to elect
a form of distribution.
15
This notice advises participants of
their right to sell company stock
and reinvest the proceeds into other
investments available under the plan.
The notice must also describe the
importance of diversifying the
investment or retirement account
assets.
See ERISA § 101(m).
IRS Notice 2006-107 provides a model
notice.
To qualify for the safe harbor, a plan
duciary must provide participants
with a SPD or SMM that describes the
plan’s automatic rollover provisions.
This must include a disclosure that if
a participant is subject to mandatory
distribution and fails to make an
election regarding a form of benet
distribution, the participant’s account
balance will be rolled over into an
individual retirement plan.
See 29 CFR § 2550.404a-2.
A plan duciary (including a qualied
termination administrator) must
provide a notice to participants and
beneciaries of the plan’s termination,
distribution options, and procedures
to make an election.
In addition, the notice must:
• provide information about the
account balance;
• explain, if known, what fees,
if any, will be paid from the
participant or beneciary’s
retirement plan; and
• provide the name, address,
and telephone number of the
individual retirement plan
provider, if known, and of the
plan administrator or other
duciary from whom information
about the termination may be
obtained.
See 29 CFR § 2550.404a-3.
Document
Type of Information
To Whom
When
Notice of Critical or Endangered Status
Participant Plan and Investment Fee
Disclosures
Plan Service Provider Disclosures
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• The bargaining parties
• PBGC
• The Department of Labor
Participants and beneciaries with
the authority to direct their own
investments in individual account
plans.
Plan duciaries responsible for hiring
pension plan service providers.
Within 30 days after the plan actuary’s
annual certification, if the actuary
certifies that the plan is in critical or
endangered status.
For a model critical status notice, see
dol.gov/sites/dolgov/files/EBSA/
about-ebsa/our-activities/public-dis-
closure/status-notices/critical/model-
notice.doc.
General information about the plan and
potential administrative and individual
costs, as well as a comparative chart of
key information about plan investment
options: Annually (at least once in any
14-month period).
Statements of the dollar amount of
administrative and individual fees that
were charged to participants’ accounts:
Quarterly.
This information may, in certain
circumstances, be included in the plan’s
SPD and participants’ Periodic Pension
Benet Statements.
Generally, reasonably in advance of
entering into a contract or arrangement
with the service provider.
See 29 CFR § 2550.408b-2(c) for
provisions on when changes or updates
to previously disclosed information
must be provided.
16
The sponsor of a multiemployer dened
benet pension plan must provide notice if
the plan is in critical or endangered status
because of funding or liquidity problems.
The notice must include an explanation
of the possibility that certain adjustable
benets may be reduced.
See IRC § 432.
These disclosures include information
about the administrative and investment
costs of participation in 401(k)-type plans.
The disclosures should include general
information about the mechanics and
structure of the plan, such as how to give
investment directions. It also includes
information about the plan’s administrative
costs (e.g., recordkeeping, legal) and
individual charges that may be assessed to
participants (for loans, QDROs, etc.).
They should also include:
• a comparative chart with information
about the plan’s investment options,
including investment fees and
expenses,
• performance and benchmark data,
• a website link that leads to
supplemental investment information,
and
• a glossary of terms to assist
participants in understanding the
plan’s investment options.
See 29 CFR § 2550.404a-5.
Certain plan service providers must
provide detailed information about the
compensation, both direct and indirect,
that they will receive for providing services
to pension plans.
Service providers may also have to provide
information to assist plans in complying
with other ERISA reporting and disclosure
requirements, such as the Form 5500
Annual Report and Participant Plan and
Investment Fee Disclosures.
See 29 CFR § 2550.408(b)-2(c) for denitions
of which service providers must comply
and the specic disclosures that must be
provided.
17
*Premium lings must be submied via PBGC’s online application, My Plan Administration Account (My PAA). Premium payments may be made online or via paper check. My PAA and
more information can be found at PBGC’s website (pbgc.gov) by clicking on Employers & Practitioners and then Premium Filings.
Overview of Basic PBGC Reporting and Disclosure Requirements
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Section 1: Pension Insurance Premiums (for covered single-employer and multiemployer dened benet plans)
(ERISA §§ 4006 and 4007; 29 CFR Parts 4006 and 4007)*
Section 2: Standard Terminations (for covered single-employer dened benet plans)
(ERISA §§ 4041 and 4050; 29 CFR Parts 4041 and 4050)
Comprehensive Premium Filing
Notice of Intent to Terminate
Form 500 - Standard Termination Notice
Notice of Plan Benets
Form 501 - Post-Distribution
Certication
This ling provides information about the
premium owed for the plan year, including
supporting data.
This provides notice about a plan’s
proposed termination and the termination
process.
This form is used to provide notice of a
plan’s proposed termination and provides
plan data.
This notice provides information on each
person’s benets.
This form is used to certify that the
distribution of plan assets has been properly
completed.
Generally, by the 15th day of the 10th
full calendar month in the plan year.
At least 60 and no more than 90 days
before the proposed termination date.
If potential insurers are not known at
this time, a supplemental notice must be
provided no later than 45 days before
distribution date.
No later than 180 days after the
proposed termination date.
No later than the time Form 500
(Standard Termination Notice) is led
with PBGC.
Within 30 days after the last distribution
date for plan benets, or within 60
days after the last distribution if email
certication is sent to PBGC within 30
days after the last distribution date.
PBGC may assess a penalty for late
ling of a Form 501 only if it is led
more than 90 days after the distribution
deadline (including extensions).
• PBGC
• Participants
• Beneficiaries
• Alternate payees
• Union
PBGC
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• Alternate payees
PBGC
18
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Section 3: Distress Terminations (for covered single-employer dened benet plans)
(ERISA §§ 4041 and 4050; 29 CFR Parts 4041 and 4050)
At least 60 days and no more than 90
days before the proposed termination
date, except with PBGC approval.
By the time Form 600 (Notice of Intent to
Terminate) is led with PBGC.
Within 15 days after the plan
administrator:
• receives an aected party’s request
for the information, or
• provides new information to PBGC
that relates to a previous request.
Concurrent with request to Bankruptcy
Court.
By the 120th day after the proposed
termination date.
PBGC
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• Alternate payees
• Union
• Participants
• Beneciaries
• Alternate payees
• Union
PBGC
PBGC
This form is used to provide notice of
a plan’s proposed distress termination,
demonstrate satisfaction of distress criteria,
and provide plan and sponsor/controlled
group data.
This notice provides notice about a plan’s
proposed distress termination and the
termination process.
A plan administrator must disclose
information it has submied to PBGC in
connection with a distress termination.
See ERISA § 4041(c)(2).
Note that a plan administrator or a plan
sponsor must also disclose information it
has submied to PBGC in connection with a
PBGC-initiated termination.
See ERISA § 4042(c)(3).
This provides notice of a sponsor’s/
controlled group member’s request to
Bankruptcy Court to approve the plan
termination based upon a reorganization
test.
This form is used to provide information
on the plan and suciency of plan assets to
provide benets.
Form 600 - Distress Termination
Notice of Intent to Terminate (NOIT)
Notice of Intent to Terminate to
Aected Parties Other than PBGC
Disclosure of Termination
Information
Notice of Request to Bankruptcy
Court to Approve Termination
Form 601 (and Schedule EA-D) -
Distress Termination Notice, Single-
Employer Plan Termination
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Form MP-100 (Missing Participants) This form is used to report information
about participants and beneciaries covered
by a terminating plan that the plan cannot
locate.
Generally, the same as the Form
501 due date. (See above for the
timing.)
PBGC
18
19
Document Type of Information To Whom When
Form 602 - Post-Distribution
Certication for Distress
Termination
Form MP-100
This form certies that the distribution of
plan assets has been properly completed
and the plan is sucient for guaranteed
benets.
This form is used to report information
about participants and beneciaries covered
by a terminating plan that the plan cannot
locate (required only if the plan is sucient
for guaranteed benets).
PBGC
PBGC
Within 30 days after the distribution of
plan assets is completed.
PBGC may assess a penalty for late ling
of a Form 602 only if it is led more than
90 days after the distribution deadline
(including extensions).
Generally, the same as the Form 602 due
date. (See above for the timing.)
Section 4: Reportable Events and Other Reports (for covered single-employer dened benet plans)
Form 10 - Post-Event Notice of
Reportable Events
Form 10-Advance - Advance Notice
of Reportable Events
This form is used to report information
relating to an event, the plan, and the
controlled group when there is a(n):
• failure to make a required contribution,
• active participant reduction,
• change in controlled group,
• application for funding waiver,
• liquidation,
• loan default, and
• various other events.
See ERISA § 4043 and 29 CFR Part 4043.
This form is used to report information
relating to an event, the plan, and the
controlled group when there is a:
• change in controlled group,
• liquidation,
• loan default,
• transfer of benet liabilities, and
• various other events.
This requirement applies to privately held
controlled groups with plans that have
aggregate unfunded vested benets over
$50 million and an aggregate funded vested
percentage under 90 percent.
See ERISA § 4043 and 29 CFR Part 4043.
Within 30 days after the plan
administrator or contributing sponsor
knows (or has reason to know) the event
has occurred.
At least 30 days before the eective date
of the event. Extensions may apply.
PBGC
PBGC
Document Type of Information To Whom When
20
Document Type of Information To Whom When
This form is used to report information
relating to the plan and controlled
group if the plan has aggregate missed
contributions of more than $1 million.
See ERISA § 302(f)(4) and 29 CFR Part
4043, subparts A and D.
These notices advise of a substantial
cessation of operations and provide
information about an employer’s election
to make additional contributions to an
aected plan.
See ERISA §§ 4062(e) and 4063(a).
This notice advises of certain withdrawals
of substantial employers and asks PBGC
to determine the resulting liability.
See ERISA § 4063(a).
This ling provides actuarial and nancial
information for certain controlled groups
with substantial underfunding.
See ERISA § 4010 and 29 CFR Part 4010.
Form 200 - Notice of Failure to Make
Required Contributions
Reporting following a Substantial
Cessation of Operations (ler may
use Form 4062(e) Series – Notices
Following a Substantial Cessation of
Operations)
Reporting of Withdrawal of
Substantial Employer
Annual Financial and Actuarial
Information Reporting
PBGC
PBGC
PBGC
PBGC
Within 10 days after the contribution
due date.
Varies depending on the event required
to be reported to PBGC.
Within 60 days after the event.
Within 105 days after the close of the
ler’s information year, with a possible
extension for certain required actuarial
information until 15 days after the ling
deadline for annual report (Form 5500).

Overview of Form 5500 and Form M-1 Annual Reporting Requirements
The Form 5500 ling requirements vary depending on whether the ler
is a small plan with fewer than 100 participants as of the beginning of the
plan year, a large plan with 100 or more participants as of the beginning
of the plan year, or a DFE.
After this section, there is a quick reference chart that describes the basic
Form 5500 ling requirements. Certain small plans may be eligible to le
the simplied Form 5500-SF instead of the Form 5500. Check the chart to
determine a plan’s eligibility.
A “one-participant” plan which is required to le the Form 5500-EZ
may elect to le online with EFAST2’s IFILE or through an EFAST2-
approved vendor rather than ling a Form 5500-EZ on paper with the
IRS. For instructions on how to le the Form 5500-EZ on paper, see the
instructions for the Form 5500-EZ which can be found at www.irs.gov/
pub/irs-pdf/i5500ez.pdf, or call the IRS at 1-877-829-5500.
The Form 5500 and the Form 5500-SF led by plan administrators and
the Form 5500 led by GIAs are due by the last day of the 7th calendar
month after the end of the plan or GIA year (not to exceed 12 months
in length). See the Form 5500 and the Form 5500-SF instructions for
information on extensions up to an additional 2 ½ months. The Form
5500 led by DFEs other than GIAs are due no later than 9 ½ months
after the end of the DFE year.
Certain employee benet plans are exempt from the annual reporting
requirements or are eligible for limited reporting options. The major
classes of plans that are exempt or eligible for limited reporting are
described in the Form 5500 and the Form 5500-SF instructions. All
welfare plans required to le Form M-1, Report for Multiple Employer
Welfare Arrangements (MEWAs) and Certain Entities Claiming
Exception (ECEs), must le an annual report in the Form 5500 Annual
Return/Report series regardless of plan size or type of funding.
1
1
See 78 Fed. Reg. 13781, 13796, 13899 (Mar. 1, 2013).
Form 5500 Annual Reporting Requirements
The Form 5500 Annual Return/Report series is used by plan
administrators and certain direct ling entities (DFEs) to satisfy annual
reporting obligations under ERISA and the Internal Revenue Code. The
Department of Labor, the IRS, and PBGC publish
• Form 5500, Annual Return/Report of Employee Benet Plan
• Form 5500-SF, Short Form Annual Return/Report of Small Employee
Benet Plan
The IRS publishes Form 5500-EZ, Annual Return of a One-Participant
Retirement Plan or a Foreign Plan.
DFEs are investment or insurance arrangements that plans can
participate in. They include:
• master trust investment accounts (MTIAs),
• bank common/collective trusts (CCTs),
• insurance pooled separate accounts (PSAs),
• 103-12 investment entities (103-12 IEs), and
• group insurance arrangements (GIAs).
All DFEs are allowed to le the Form 5500 directly with EBSA, but it is
mandatory for MTIAs. If an employee benet plan participates in a CCT,
PSA, 103-12 IE, or GIA that les a Form 5500 as a DFE, then it is eligible
for certain annual reporting relief in connection with the plan’s own
Form 5500 ling requirement.
All Forms 5500 and Forms 5500-SF must be led online using the ERISA
Filing Acceptance System (EFAST2). Filers may use EFAST2’s web-based
IFILE ling system or an EFAST2-approved vendor. All delinquent and
amended lings of Title I plans must also be submied through EFAST2.
More information about ling with EFAST2 is available at efast.dol.gov.
21
Check the EFAST website at efast.dol.gov and the latest Form 5500
and Form 5500-SF instructions for information on who is required to
file, how to complete the forms, when to file, EFAST2-approved
software, and electronic filing options. You can also visit dol.gov/
agencies/ebsa/key-topics/reporting-and-filing/form-5500 to view the
Form 5500 and the Form 5500-SF. Schedules and instructions are also
posted on that website.
Form M-1 Annual Reporting Requirements
Administrators of multiple employer welfare arrangements (MEWAs)
and certain other entities that oer or provide medical care coverage
to employees of two or more employers are generally required to le
the Form M-1, Report for Multiple Employer Welfare Arrangements
(MEWAs) and Certain Entities Claiming Exception (ECEs). After this
section, there is a quick reference chart on reporting requirements for
MEWAs and ECEs.
The Form M-1 must be
led online using the M-1 Online Filing System.
You can le the Form M-1 and nd more information, including
frequently asked questions, at askebsa.dol.gov/mewa.
22
Large Pension Plan Small Pension Plan
2
Small Welfare Plan
2
Large Welfare Plan DFE
Form 5500
Schedule A
(Insurance Information)
Schedule C (Service
Provider Information)
Schedule D (DFE/
Participating Plan
Information)
Schedule G (Financial
Schedules)
Schedule H (Financial
Information)
Schedule I
(Financial Information)
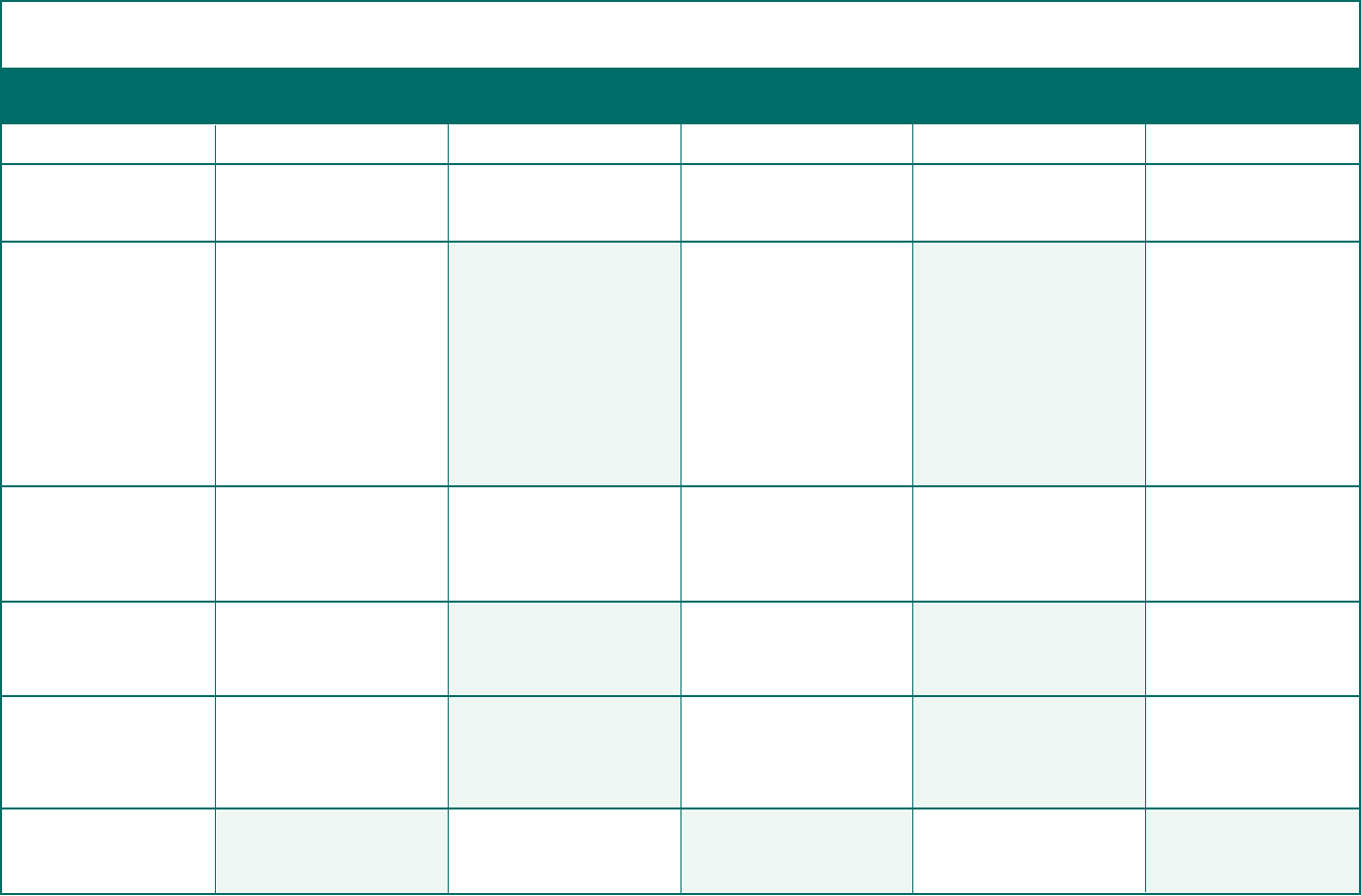
Must complete.
3
Must complete if plan has
insurance contracts.
Must complete Part I if
service provider was paid
$5,000 or more, Part II if
a service provider failed
to provide information
necessary for the
completion of Part I, and
Part III if an accountant or
actuary was terminated.
Must complete Part I if plan
participated in a CCT, PSA,
MTIA, or 103-12 IE.
Must complete if Schedule
H, lines 4b, 4c, or 4d are
“Yes.”
3
Must complete.
3, 5
Not required.
Must complete.
Must complete if plan has
insurance contracts.
Must complete Part I if
service provider was paid
$5,000 or more, Part II if
a service provider failed
to provide information
necessary for the
completion of Part I, and
Part III if an accountant or
actuary was terminated.
Must complete Part I if plan
participated in a CCT, PSA,
MTIA, or 103-12 IE.
Must complete if Schedule
H, lines 4b, 4c, or 4d are
“Yes.”
Must complete.
5
Not required.
Must complete.
Must complete if plan has
insurance contracts.
4
Not required.
Must complete Part I
if plan participated in
a CCT, PSA, MTIA, or
103-12 IE.
4
Not required.
Not required.
Must complete.
4
Must complete.
3
Must complete if plan has
insurance contracts.
4
Not required.
Must complete Part I if plan
participated in a CCT, PSA,
MTIA, or 103-12 IE.
4
Not required.
3
Not required.
Must complete.
4
Must complete.
Must complete if MTIA,
103-12 IE, or GIA has
insurance contracts.
MTIAs, GIAs, and
103-12 IEs must complete
Part I if service provider
paid $5,000 or more,
and Part II if a service
provider failed to provide
information necessary
for the completion of
Part I. GIAs and 103-12
IEs must complete Part
III if accountant was
terminated.
All DFEs must complete
Part II, and DFEs that
invest in a CCT, PSA,
or 103-12 IE must also
complete Part I.
Must complete if
Schedule H, lines 4b, 4c,
or 4d for a GIA, MTIA, or
103-12 IE are “Yes.”
All DFEs must complete
Parts I, II, and III. MTIAs,
103-12 IEs, and GIAs
must also complete Part
IV.
5
Not required.
23
Quick Reference Chart of Form 5500, Schedules, and Attachments (Not Applicable for Form 5500-SF Filers)
*1
*See footnotes for certain exemptions and other technical requirements. All footnotes for this chart are on page 24.
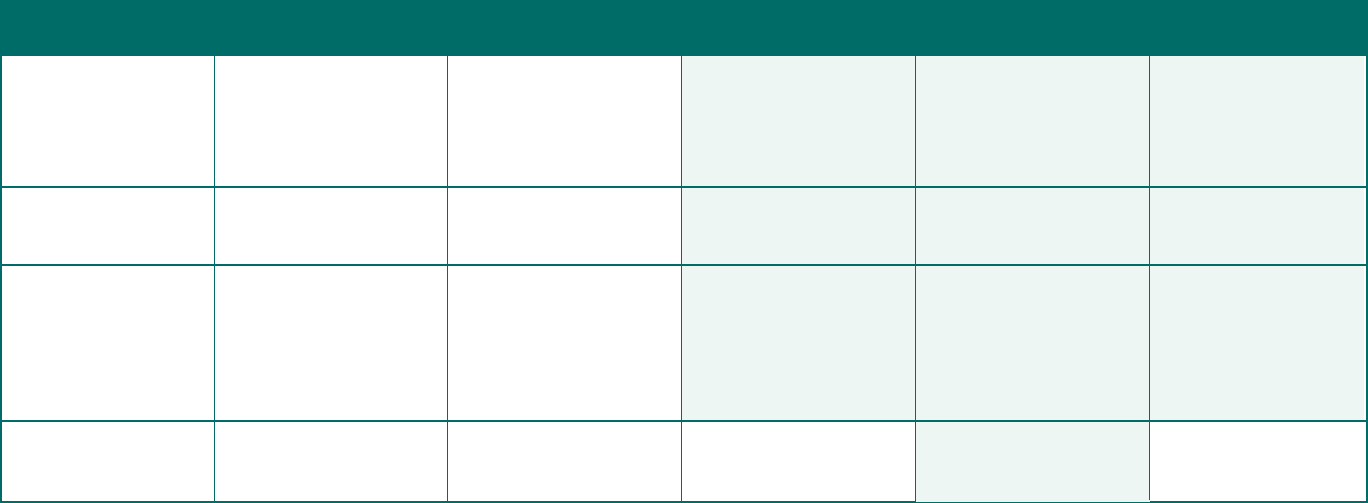
Large Pension Plan Small Pension Plan
2
Small Welfare Plan
2
Large Welfare Plan DFE
Schedule MB
(Actuarial Information)
Schedule R
(Pension Plan
Information)
Schedule SB
(Actuarial Information)
Accountant’s Report
Must complete if
multiemployer dened
benet plan or money
purchase plan subject
to minimum funding
standards.
6
Must complete.
7
Must complete if
single-employer or
multiple-employer dened
benet plan, including an
eligible combined plan
and subject to minimum
funding standards.
Must aach.
Must complete if
multiemployer dened
benet plan or money
purchase plan subject
to minimum funding
standards.
6
Must complete.
4, 7
Must complete if
single-employer or
multiple-employer dened
benet plan, including an
eligible combined plan
and subject to minimum
funding standards.
Not required unless
Schedule I, line 4k, is
checked “No.”
Not required.
Not required.
Not required.
Must aach.
3
Not required.
Not required.
Not required.
Not required.
1
This chart provides only general guidance. Not all rules and requirements are reected. Refer to specic Form 5500 instructions for complete information on ling requirements (e.g., Who Must File and What To File). For
example, a pension plan is exempt from ling any schedules if the plan uses Code section 408 individual retirement accounts as the sole funding vehicle for providing benets. See Limited Pension Plan Reporting.
2
Pension plans and welfare plans with fewer than 100 participants at the beginning of the plan year that are not exempt from ling an annual return/report may be eligible to le the Form 5500-SF, a simplied report.
In addition to the limitation on the number of participants, a Form 5500-SF may only be led for a plan that is exempt from the requirement that the plan’s books and records be audited by an independent qualied
public accountant (but not by reason of enhanced bonding), has 100 percent of its assets invested in certain secure investments with a readily determinable fair market value, holds no employer securities, and is not a
multiemployer plan. See Who Must File.
3
Unfunded, fully insured, or combination unfunded/fully insured welfare plans covering fewer than 100 participants at the beginning of the plan year that meet the requirements of 29 CFR 2520.104-20 are exempt
from ling an annual report. See Who Must File. Such a plan with 100 or more participants must le an annual report, but is exempt under 29 CFR 2520.104-44 from the accountant’s report requirement and completing
Schedule H, but MUST complete Schedule G, Part III, to report any nonexempt transactions. See What to File. All Plans required to le Form M-1, Report for Multiple-Employer Welfare Arrangements (MEWAs) and Certain
Entities Claiming Exception (ECEs) must le a Form 5500 regardless of plan size or type of funding.
4
Do not complete if ling the Form 5500-SF instead of the Form 5500.
5
Schedules of assets and reportable (5%) transactions also must be led with the Form 5500 if Schedule H, line 4i or 4j is “Yes.”
6
Money purchase dened contribution plans that are amortizing a funding waiver are required to complete lines 3, 9, and 10 of the Schedule MB in accordance with the instructions. Also see instructions for line 5 of
Schedule R and line 12a of Form 5500-SF.
7
Schedule R should not be completed when the Form 5500 Annual Return/Report is led for a pension plan that uses, as the sole funding vehicle for providing benets, individual accounts or annuities (as described in
Code section 408). See the Form 5500 instructions for Limited Pension Plan Reporting for more information.
Not required.
Not required.
Not required.
Must aach for a GIA or
103-12 IE.
24
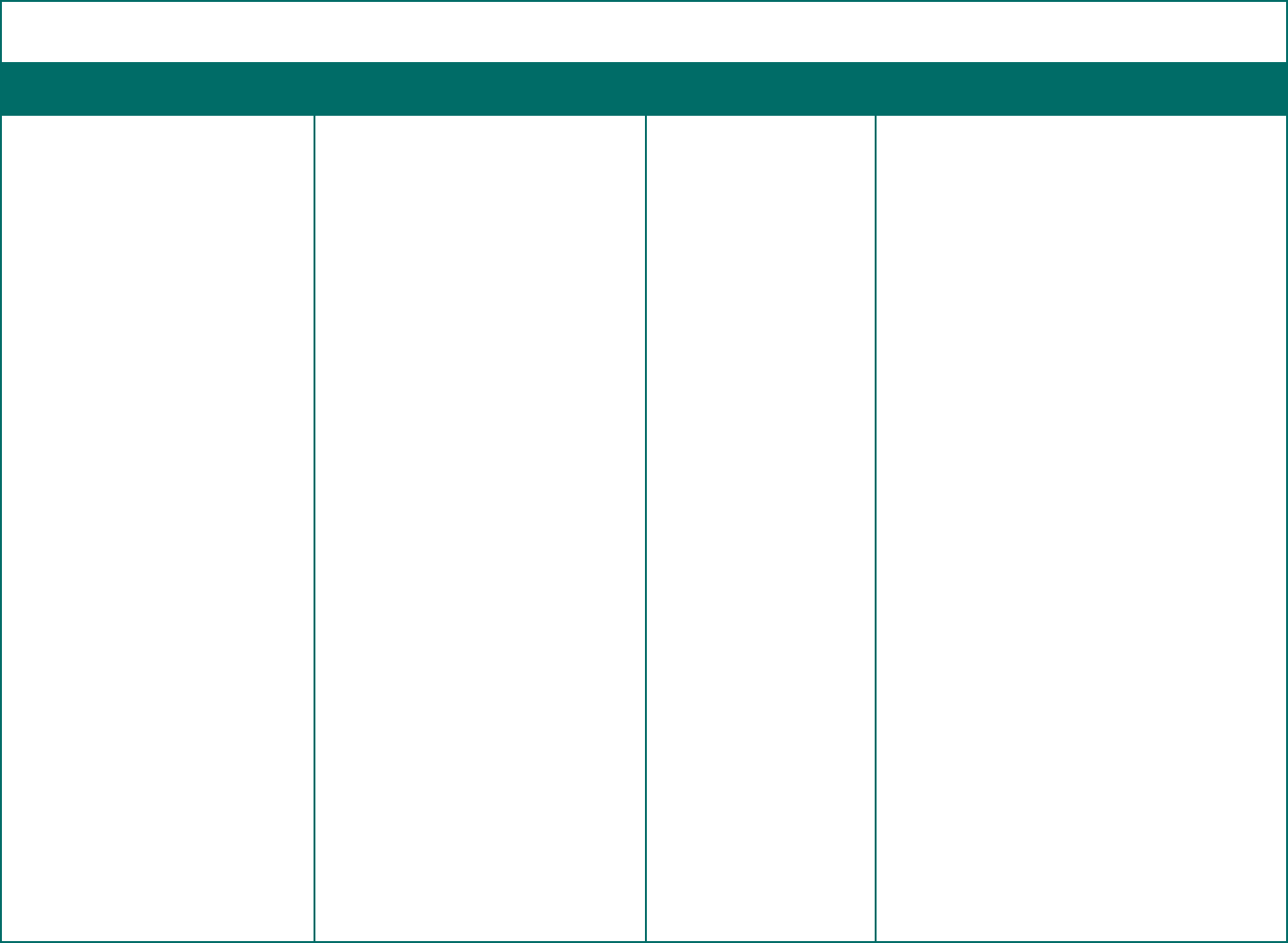

Document Type of Information To Whom When
MEWAs and ECEs Quick Reference Chart: Form M-1
1
This form includes:
• MEWA or ECE custodial and nancial
information,
• states in which coverage is provided,
• insurance information,
• number of participants covered,
• information about enforcement actions,
and
• information about compliance with Part
7 of ERISA, including any litigation
alleging non-compliance.
Administrators of MEWAs and ECEs that
oer or provide coverage for medical care
to employees of two or more employers
(including one or more self-employed
individuals) are generally required to le the
Form M-1.
An ECE is an entity that claims it is not a
MEWA due to the exception in the denition
of MEWA for entities that are established
and maintained under or pursuant to one or
more agreements that the Secretary of Labor
nds to be collective bargaining agreements.
An ECE must le this report during the rst
three years after the ECE is originated. For
more information on this exception, see 29
CFR § 2510.3-40.
1
This chart provides only general guidance, and not all rules and requirements are reected.
Form M-1
Report for Multiple Employer Welfare
Arrangements (MEWAs) and Certain
Entities Claiming Exception (ECEs)
EBSA
25
Annual Report
Generally, due by March 1st of the year after the
calendar year for which report is required. A
60-day extension is available.
For ECEs, an annual report is required to be led
only if the ECE was last originated within the 3
years before the annual ling due date.
MEWA Registration
A MEWA may have to register more than once
during the reporting year. MEWA registration
generally is required:
• 30 days before operating in any state
• Within 30 days of knowingly operating
in any additional state or states that were
not indicated on a previous Form M-1
ling
• Within 30 days of operating with regard
to the employees of an additional
employer (or employers, including one or
more self-employed individuals) after a
merger with another MEWA
• Within 30 days of the date the number of
employees receiving coverage for
medical care under the MEWA is at least
50 percent greater than the number of
such employees on the last day of the
previous calendar year
• Within 30 days of experiencing a material
change as dened in the Form M-1
instructions
ECE Origination
An ECE may be originated more than once during
the reporting year. ECE origination lings generally
must be made:
• 30 days before operating with regard to
the employees of two or more employers
(including one or more self-employed
individuals)
• Within 30 days from when ECE begins
operating following a merger with
another ECE (unless all of the ECEs that
participate in the merger previously were
last originated at least 3 years prior to the
merger)
• Within 30 days from when the number of
employees receiving coverage for
medical care under the ECE is at least 50
percent greater than the number of such
employees on the last day of the previous
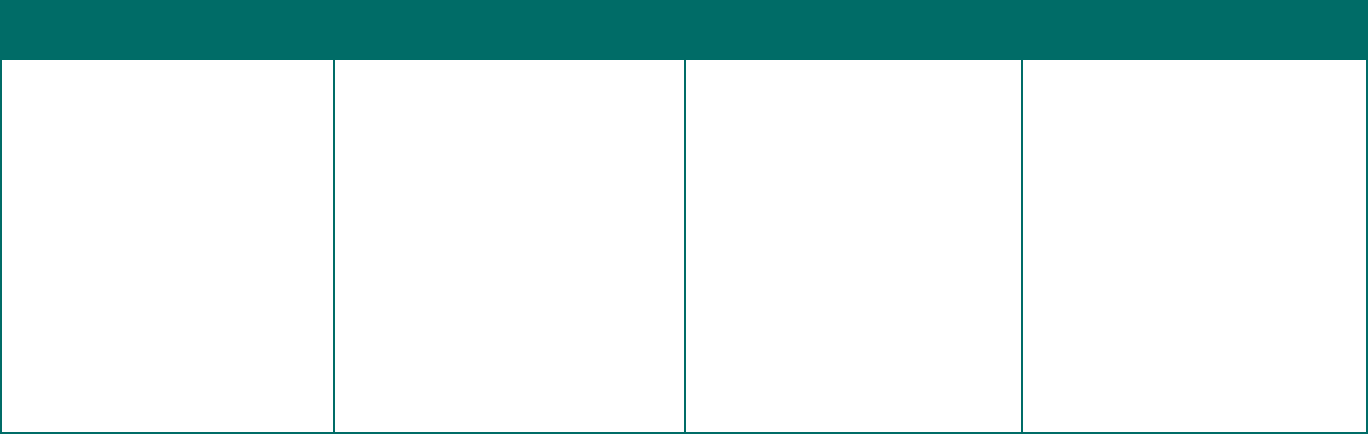
Document Type of Information To Whom When
26
calendar year (unless the increase
is due to a merger with another
ECE under which all ECEs that
participate in the merger were last
originated 3 years prior to the
merger).
ECE Special Filing
Due within 30 days of a special ling event,
only if the ECE was last originated within 3
years before a special ling event. Special
ling events, which may occur more than
once during the reporting year, include:
• The ECE begins knowingly
operating in any additional state
or states that were not indicated
on a previous Form M-1 ling.
• The ECE experiences a material
change as dened in the Form M-1
instructions.
EBSA Resources
For more information about EBSA’s reporting and disclosure
requirements, contact:
U.S. Department of Labor
Employee Benets Security Administration
200 Constitution Ave., N.W.
Washington, DC 20210
1-866-444-3272
Website: dol.gov/ebsa
For assistance completing the Form 5500, call the EFAST2 Help Desk at
1-866-463-3278.
For more information on the Form 5500, visit dol.gov/agencies/ebsa/key-
topics/reporting-and-ling/form-5500.
For assistance completing the Form M-1, call (202) 693-8360.
The following publications may be helpful in providing a more detailed
explanation on specic subject maer:
An Employer’s Guide to Group Health Continuation Coverage
Under COBRA
QDROs: The Division of Retirement Benets Through Qualied Domestic
Relations Orders
Troubleshooter’s Guide to Filing the ERISA Annual Report (Form 5500)
These and other EBSA publications may be obtained by calling toll-free
at 1-866-444-3272 or visiting dol.gov/agencies/ebsa/about-ebsa/our-
activities/resource-center/publications.
PBGC Resources
For information about PBGC’s reporting and disclosure requirements,
call 1-800-736-2444 or (202) 326-4242.
To request information or assistance via email, use the applicable email
address shown below:
• Premiums: [email protected]
• Reportable events: [email protected] or advancereport@
pbgc.gov
• 4010 lings: [email protected]
• Standard Terminations: [email protected]
• Distress terminations: [email protected]
For other topics, see PBGC’s practitioner contact email list at: pbgc.gov/
about/pg/contact/contact-prac.
To request assistance via mail or delivery service, write to:
Pension Benet Guaranty Corporation
445 12 Street SW
Washington, DC 20024-2101
Aention: [insert applicable department name]
For questions on distress terminations, reportable events and 4010
lings, you can also call 202-229-4070 or write to us at the address above
and add Aention: Corporate Finance and Restructuring Department.
For additional information, visit PBGC’s website: pbgc.gov
27


